Catamaran Sailboats: Twin-Hull Performance and Comfort
Experience twin-hulled catamarans, where stability meets spacious design. These modern sailing vessels excel in both comfort and performance.
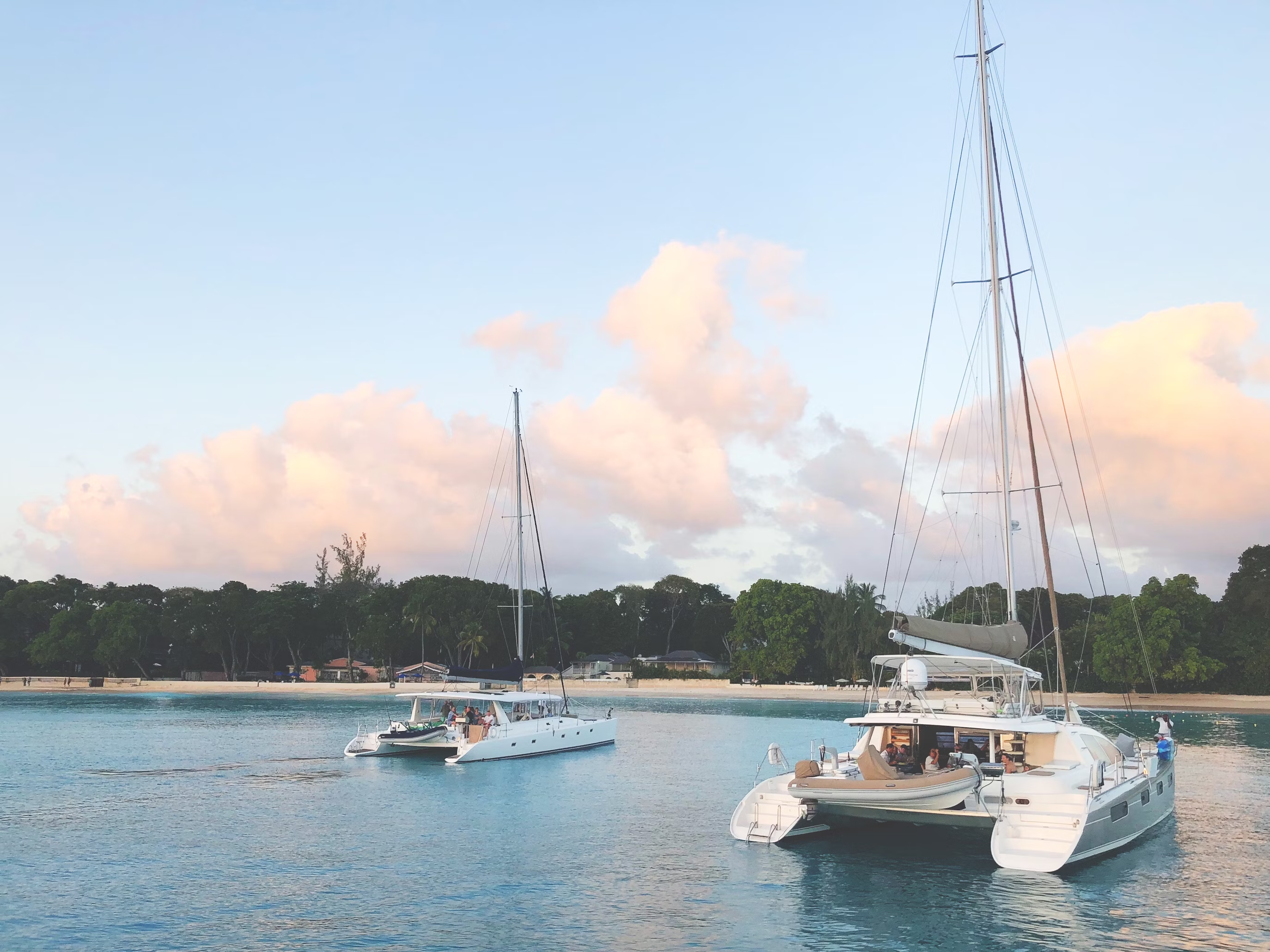
Catamaran example
Catamarans are twin-hulled sailing vessels that offer exceptional stability, speed on certain points of sail, and generous living space. Their modern design combines performance with comfort, making them increasingly popular for both private ownership and charter operations, particularly in coastal and tropical environments where their shallow draft and stable platform provide significant advantages. While the basic concept of multiple hulls dates back to ancient Polynesian cultures, modern sailing catamarans emerged in the 1960s and gained significant popularity in the 1990s. Originally developed from traditional Pacific island designs, contemporary catamarans have evolved through racing innovations and cruising adaptations. The breakthrough designs of Nathanael Herreshoff in the late 1800s and subsequent developments by James Wharram in the 1950s helped establish catamarans as viable alternatives to traditional monohulls.
| Key Characteristics | Use Cases |
|---|---|
|
|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|